drop arm testing|drop arm test pdf : exporters Sensitivity of detecting a full thickness supraspinatus tear is 73% The specificityis 77% The Likelihood Ratio is 6.45 (95% CI=2.25–18.47) See more u/amandaleonn: Welcome to my page!! 💕I'm Amanda I have high standards and a dirty mind. Are you up for the challenge? 😈 I get a ton of messages here.
{plog:ftitle_list}
• At the Internet Movie Database• A blog about La Hora Marcada series - Compiled by Luis Pedro Cabrera Ver mais
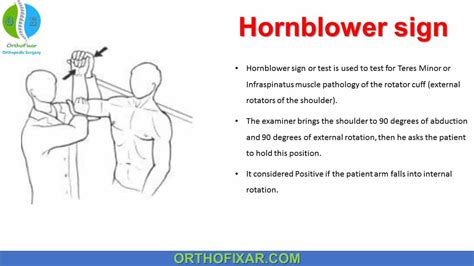
positive hornblower's sign
doxycycline for hard test knot
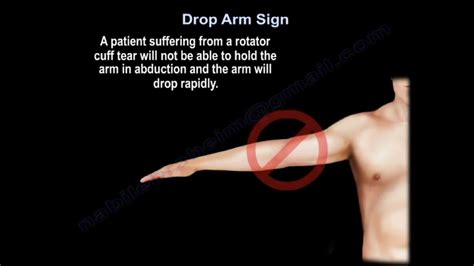
positive drop arm sign
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus . This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when . See moreThe test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without their symptoms occurring . It is a positive test if there is a sudden dropping of the arm or weakness in maintaining arm position during the eccentric part of abduction. There . See moreIt was found that it is unclear if a full thickness rotator cuff tear can be diagnosed by using any of the cluster of lag signs, let alone solely the drop arm sign . All lag sign tests for rotator cuff integrity have been shown to have high specificity, but low . See more
Sensitivity of detecting a full thickness supraspinatus tear is 73% The specificityis 77% The Likelihood Ratio is 6.45 (95% CI=2.25–18.47) See moreThis page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included. A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm.
Drop Arm Test / Sign | Supraspinatus Tear. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP: 📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w 🤖 Android: . The drop arm test is a physical examination test used by healthcare professionals to assess shoulder pain and potential rotator cuff injuries. It is typically .
dpd hardness test
The drop arm test is designed to determine a patient's ability to sustain humeral joint motion through eccentric contraction as the arm is taken through the full motion of abduction to .The Drop Arm Sign or Drop Arm Test is a common orthopedic test to assess for full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus.Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign. 2. Drop Arm Test. A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially if any one of the 4 stabilizers of the rotator cuff are compromised. To .
The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tear. Read how to perform the drop arm test. Drop-arm test. How it’s performed: You will raise your arms to the side as high as possible and lower them to 90 degrees. What it tests for: Torn rotator cuff. This Technique Peek video features Frank Hoeffner, DPT, OCS demonstrating how to perform drop arm test for the shoulder. This test is performed by passively .
Drop Arm Test. A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially if any one of the 4 stabilizers of the rotator cuff are compromised. To perform the drop arm test, simply raise your arm overhead in an arc, with as much range as possible. Now reverse the arc and lower your arm slowly, without assistance.
A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11). Among the six pain .
The drop arm test is a specific test for assessing supraspinatus muscle function, as it requires the muscle to hold the arm in an abducted position against the force of gravity. If the muscle is torn or weak, it is unable to generate enough force to maintain the arm in the horizontal position, resulting in a positive drop arm test.
Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is told to actively elevate the arm in the scapular plane, followed by slowly reversing the motion.The test is positive if the arm drops suddenly or the patient experiences pain. Diagnostic Accuracy: Sensitivity: 7.8; Specificity: 97.2; +LR: 2.79 .
When the drop arm test is used for a series of experiments like these, it could be more accurate: Empty or fully testable. Lag indicator for external rotation. Lag indicator for internal rotation. The Hornblower sign. To discriminate between rotator cuff muscles and provide a more reliable diagnosis, a battery of tests should be conducted.The Drop-Arm Sign. Patient actively elevates the arm in the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion. A positive test is defined as the patient experiencing pain during the activity or that the arm suddenly drops. The Painful Arc Sign (Fig 1) Patient fully elevates the arm along the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion.Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, . Drop Arm Test / Codman's Test; Empty Can Test; Full Can Test; Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) and shoulder impingement strength is assessed using Jobe’s Test (see below) – pain with this test is indicative of a subacromial bursitis/irritation – not necessarily a tear. Only considered positive for tear with a true drop arm. i.e. arm is brought to 90° and literally falls down.
For a positive test, however, the patient would not be able to hold this position and their arm may spring back anteriorly, indicating that the teres minor and the infraspinatus are weak or painful. 2. The examiner supports the elbow and holds the arm in external rotation at the wrist. 3.
The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. To perform the Drop Arm test, position the patient in sitting or standing with the arm relaxed at their side. The examiner passively places the patient’s arm into abduction of 90 degrees. The patient is instructed to lower . Sensitivity & Specificity. A literature review 1 in MEDLINE was performed for physical examination tests/maneuvers of the rotator cuff tears, and found that drop arm sign has the following accuracy:. Sensitivity: 73 %; Specificity: 98 %; Another study by Walch G 2 found that this test has a 100% sensitivity and a 100% specificity for irreparable degeneration of the .Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return . Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive test; Drop Arm Test video provided by Clinically Relevant. Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation.
The drop arm test is a physical examination maneuver used to assess for full-thickness rotator cuff tears. It is performed by asking the patient to actively lift their arm to shoulder level, then slowly lower it back down to their . Drop Arm Test is an orthopedic maneuver used to help diagnose injury to the rotator cuff. A positive test will involve the inability to gradually lower the .
The drop arm test also cannot be used as a screening test due to its low sensitivity. This paradigm also applies to the lag signs for infraspinatus tears. Data from this study shows near perfect specificity and a low sensitivity for lag signs.
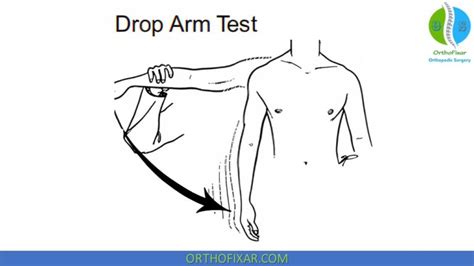
Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of shoulder abduction in the scapular plane. The examiner initially supports the limb and then instructs the patient to adduct the arm to the side of the body slowly. A positive test includes the patient’s inability to maintain the abducted position of the .
The first is a drop test: the clinician drops the “paralyzed” arm over the patient's face. In pseudoneurologic syndrome, the “paralyzed” arm will not strike the patient's face when dropped .
Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.16. Codman's Test, also known as the Drop Arm Test, is a physical examination maneuver used to assess a suspected rotator cuff tear. It is used to evaluate the integrity of the supraspinatus tendon and muscle, which is commonly injured in rotator cuff tears. Drop arm test. Pain with Jobe test. Infraspinatus. ER weakness at 0° abduction. ER lag sign. Teres minor. ER weakness at 90° abduction and 90° ER. Hornblowers. . allows for dynamic testing. inexpensive. readily available at most centers. helpful to confirm intraarticular injections. disadvantages include.
The patient's arm is passively elevated to 90 degrees in the scapular plane, by the examiner; The examiner passively flexes the elbow to 90 degrees; The patient is asked to actively externally rotate the shoulder against the examiner's resistance; Another method for performing the test, introduced by McClusky, helps depict the Hornblower's sign: - Push off demonstrating winging of scapula - Apley scratch tests for shoulder motion - Drop arm test - External rotation testing of shoulder - Passive Painful Arc Neer Test - Scapular assistance maneuver - Sulcus sign for glenohumeral instability examination - Apprehension relocation release tests for shoulder Drop Arm Test . Your healthcare provider may perform the drop arm test if they think you may have a rotator cuff tear in your shoulder. For this test, the provider will lift your arm out to the side of your body while keeping it straight. .If the patient can lower the arm without problem, the test should be performed again and the examiner should apply a slight tap on the forearm when the arm is abducted at 90 0. Positive Test: This test will be positive if the patient can not control the adduction movement of the arm and the arm drops to the patient’s side.
Drop arm test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without pain. Drop arm test is positive if there is pain while lowering the arm, sudden dropping of the arm or weakness in maintaining arm position during lowering (with or without pain), suggesting injury to the supraspinatus 1 .
Resultado da 15 de set. de 2023 · 81 views 4 months ago. Get ready for an exclusive peek into the lives of the Roloff family's dynamic duo, Tori and Audrey Roloff, .
drop arm testing|drop arm test pdf